Baseball fans love stats. One key stat is the average runs per game.
This number shows how many runs teams score each game over a season. Understanding how this average changes over the years can be fascinating. It reveals trends and shifts in the game. Sometimes, high scores reflect strong batting. Other times, low scores show great pitching.
By looking at MLB average runs per game by year, we can see the evolution of baseball. This data can show when the game was more about home runs or when pitching dominated. Let’s dive into the history and see what these numbers tell us about America’s pastime.
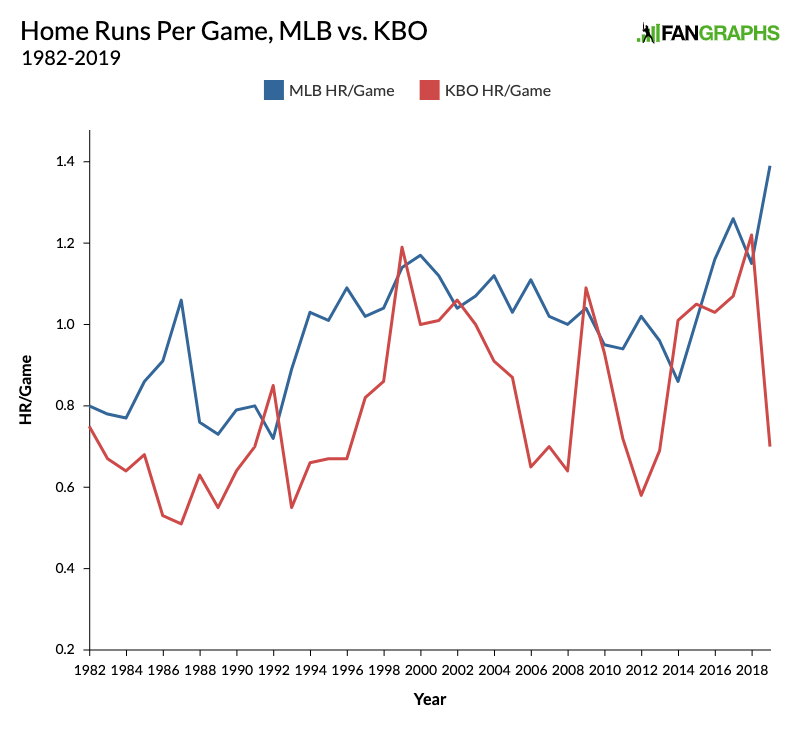
Credit: blogs.fangraphs.com
Early Years Of Mlb
The early years of MLB were a time of formation and growth. The league, with its rich history, saw many changes in gameplay and scoring. Understanding these trends gives insight into the evolution of baseball.
Formation Of The League
In the late 19th century, baseball began to take shape. The National League was established in 1876, followed by the American League in 1901. These leagues formed the foundation of Major League Baseball.
During this period, the rules of the game were still evolving. Pitching distances, ball sizes, and other elements were not standardized. This led to varied scoring patterns across teams and seasons.
Initial Scoring Trends
Scoring in the early years of MLB was quite different from today. In the late 1800s, games often featured low scores. Teams struggled to score runs due to the primitive equipment and fields.
As the game progressed, scoring began to increase. The introduction of new rules and better equipment played a significant role. For example, in the early 1900s, the average runs per game started to rise steadily.
| Year | Average Runs Per Game |
|---|---|
| 1876 | 3.94 |
| 1900 | 4.50 |
| 1920 | 5.13 |
By examining the average runs per game, one can see the evolution of scoring trends. The early years set the stage for the dynamic and high-scoring games we enjoy today.
Dead-ball Era
The Dead-Ball Era in MLB saw low average runs per game. This period spanned from 1900 to 1919. Teams scored fewer runs, making games less high-scoring.
The Dead-Ball Era, spanning from the early 1900s to 1919, is a fascinating period in Major League Baseball history. This era is named for the low-scoring games and the lack of home runs. Many fans and historians find it intriguing because it contrasts sharply with modern baseball’s high-scoring games.
Characteristics
The Dead-Ball Era featured heavy, soft baseballs. These balls did not travel far when hit. Pitchers had an advantage due to the ball’s condition. They could use spitballs and other tricks to control the game. Stadiums were larger, making home runs rare. Instead, teams focused on strategy. Bunting, stealing bases, and hit-and-run plays were common. Defense was also crucial. Players had to be sharp and quick.
Impact On Scoring
Scoring during the Dead-Ball Era was low. Teams averaged around 3 to 4 runs per game. Pitchers often dominated. Some even had earned run averages (ERAs) below 2.00. Fans saw many 1-0 or 2-1 games. This made each run significant. Managers needed to be clever. They had to find ways to score without relying on power hitting. This era shaped baseball’s history. It showed the importance of strategy and skill. It also laid the groundwork for future changes in the game.
Live-ball Era
The Live-Ball Era in Major League Baseball (MLB) began in 1920. This era marked a significant change in how the game was played. The introduction of new rules and an emphasis on offense led to an increase in the average runs per game.
Introduction Of New Rules
The Live-Ball Era brought new rules that changed the game. Before 1920, pitchers had more control over the ball. They could use substances to alter its movement. This made it harder for batters to hit. In 1920, MLB banned these practices. This made the ball more predictable and easier to hit.
Another rule change was the introduction of fresh balls during games. Previously, balls were reused until they were too dirty to see. Clean, fresh balls were easier to hit and increased the number of runs scored.
Rise In Offensive Play
The new rules led to a rise in offensive play. Batters took advantage of the predictable balls and clean, fresh ones. This made home runs more common. Home runs became a significant part of the game.
Let’s look at some data to see the impact:
| Year | Average Runs Per Game |
|---|---|
| 1920 | 4.36 |
| 1930 | 5.55 |
| 1940 | 4.68 |
As the data shows, the average runs per game increased during the Live-Ball Era. This trend continued in the following decades.
The rise in offensive play also changed how teams were built. Teams began to focus on players who could hit home runs. Power hitters became more valuable.
- More home runs
- Higher average runs per game
- Focus on power hitters
The Live-Ball Era was a turning point in MLB history. The rule changes and rise in offensive play shaped the modern game.
Post-world War Ii Period
The Post-World War II period brought significant changes to Major League Baseball (MLB). This era, spanning from 1945 onwards, saw a transformation in gameplay and scoring patterns. The average runs per game fluctuated, reflecting these changes. Fans witnessed both low-scoring and high-scoring seasons, each with its own unique characteristics.
Changes In Gameplay
After World War II, MLB teams made key adjustments in their strategies. Managers focused more on offensive plays. They trained players to hit for power. This led to an increase in home runs. Pitchers also adapted their techniques, resulting in varied game outcomes.
Stadiums became more player-friendly. Some ballparks shortened their fences. This further boosted scoring opportunities. Advanced training methods and better equipment also played a role. Players became stronger and more skilled. These changes collectively influenced the average runs per game.
Notable High-scoring Seasons
The late 1940s and early 1950s were notable for high-scoring games. In 1949, the average runs per game peaked. Teams scored an average of 4.61 runs per game. This was one of the highest in history.
Another remarkable year was 1950. Teams scored even more. The average reached 4.85 runs per game. This was due to stronger batting lineups and weaker pitching.
These high-scoring seasons thrilled fans. They enjoyed the excitement of frequent runs. The Post-World War II period left a lasting impact on MLB’s scoring trends. Fans still talk about these memorable seasons.
Modern Era Trends
The Modern Era of Major League Baseball (MLB) has seen many changes. These changes have impacted the average runs per game each year. Understanding these trends helps us see how the game has evolved.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have played a key role in baseball. Equipment has improved, helping players perform better. Bats are now lighter and more durable. This allows players to hit the ball harder and farther.
Pitches can be analyzed in real-time. High-speed cameras track every pitch. This gives pitchers data to improve their techniques. Hitters also benefit. They can study the pitches they will face. This data helps them make better contact with the ball.
Influence Of Analytics
Analytics have changed how teams play baseball. Teams use data to make decisions during games. This includes when to bunt, steal bases, or shift defensive positions.
- Sabermetrics: This is the study of baseball statistics. It helps teams find the best players.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Teams use data to decide their lineups. They analyze player performance to create the best matchups.
Teams also use data to manage pitchers. They track pitch counts to avoid injuries. This keeps pitchers healthy and effective throughout the season.
| Year | Average Runs Per Game |
|---|---|
| 2010 | 4.38 |
| 2015 | 4.25 |
| 2020 | 4.65 |
| 2023 | 4.78 |
As you can see, the average runs per game have varied. Technology and analytics have influenced these numbers. They have made the game more strategic and competitive.
Comparative Analysis
Analyzing the average runs per game in MLB over the years gives insights into the game’s evolution. This analysis looks at how runs per game have changed over decades. It also examines the factors influencing these variations.
Decade-by-decade Comparison
In the 1920s, MLB saw a surge in runs per game. This was known as the “live-ball era.” During the 1930s, the average runs per game continued to rise. This trend changed in the 1940s when runs per game dropped. The reason was World War II, which affected player availability.
The 1950s and 1960s witnessed a slight increase in runs. However, the 1970s and 1980s saw a decline again. The 1990s brought another rise in runs per game. Steroid use and smaller ballparks played a role in this increase. In the 2000s and 2010s, runs per game fluctuated but remained relatively high.
Factors Influencing Variations
Many factors influence the average runs per game. Rule changes impact how the game is played. Changes in pitching styles and strategies also matter. Player fitness and training routines have evolved over time. The construction of ballparks affects game outcomes. Smaller parks often lead to more home runs.
Technological advancements and data analytics influence gameplay. Teams now use data to improve strategies. Weather conditions can also play a role. Hotter weather often results in more runs. Player equipment and training methods have improved. This has also led to variations in runs per game.
Future Projections
Major League Baseball (MLB) has seen many changes over the years. The average runs per game is a key statistic. It shows how the game evolves. Predicting future trends can help fans and teams alike. Let’s dive into what the future might hold for MLB scoring.
Emerging Trends
Several trends are shaping the future of MLB scoring. One major trend is the emphasis on analytics. Teams use data to improve their strategies. This includes optimizing batting orders and pitcher selections. As a result, scoring patterns could change.
Another trend is the focus on player health. Improved training and recovery methods could lead to more consistent performances. Healthier players might score more runs. This would increase the average runs per game.
Technology is also playing a big role. Advanced training tools and equipment help players improve their skills. Better hitters and pitchers can affect the scoring dynamics. These emerging trends suggest a shift in how games will be played and scored.
Potential Changes In Scoring
Changes in scoring rules and strategies may impact future averages. One possibility is adjustments to the strike zone. Altering the strike zone could make it easier or harder to score runs.
Another potential change is the introduction of new technologies. Automated strike zones and enhanced replay systems could affect game outcomes. These technologies aim to make calls more accurate. This could lead to fairer games with different scoring patterns.
Player development is also crucial. Teams invest heavily in developing young talent. Better training programs and facilities can produce more skilled players. This can lead to higher average runs per game.
Here is a table showing possible changes and their impact:
| Change | Impact on Scoring |
|---|---|
| Adjusting Strike Zone | May increase or decrease runs |
| New Technologies | More accurate calls, varied scoring |
| Player Development | Higher skill levels, more runs |
These changes could shape the future of MLB scoring. Fans and analysts should keep an eye on these developments. The game we love continues to evolve.
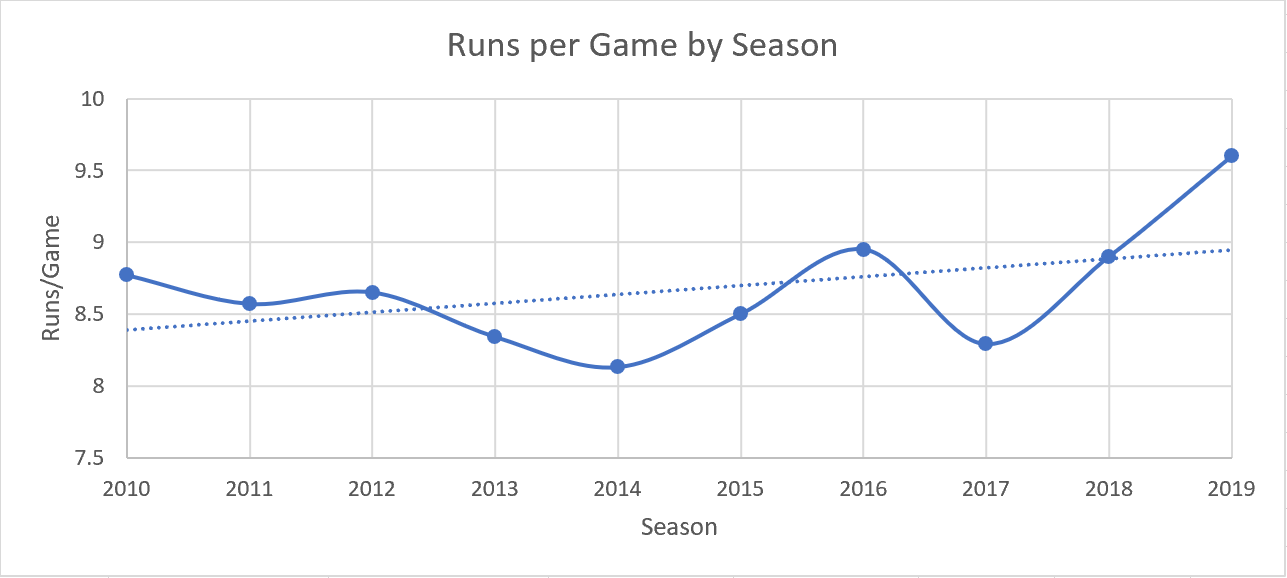
Credit: www.samford.edu
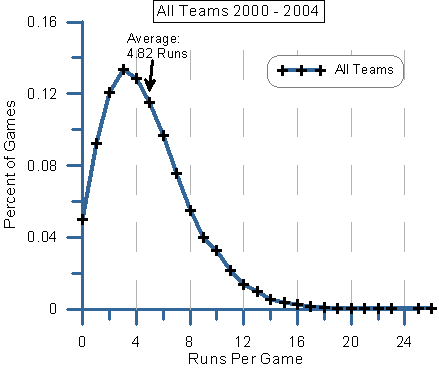
Credit: tht.fangraphs.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Average Mlb Runs Per Game?
The average MLB runs per game varies by year. Generally, it ranges from 8 to 10 runs combined.
How Have Mlb Runs Per Game Changed?
MLB runs per game have fluctuated over the years. Factors include changes in pitching, hitting, and rule adjustments.
What Affects Mlb Average Runs Per Game?
Factors include pitching quality, player performance, weather conditions, and rule changes. These variables impact scoring.
Which Year Had The Highest Mlb Runs Per Game?
The 1930 season had the highest runs per game. Teams averaged around 11 runs combined per game.
Conclusion
The average runs per game in MLB have changed over the years. These changes reflect shifts in strategies, player skills, and game dynamics. Fans and analysts alike find these trends intriguing. Understanding these patterns helps appreciate the sport better. Keeping an eye on these stats adds depth to watching games. Baseball remains exciting and unpredictable. Stay tuned for more thrilling seasons ahead.






